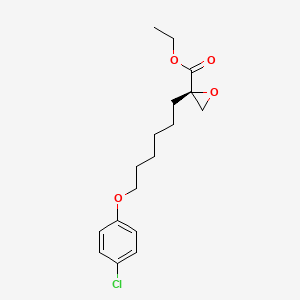
(R)-Ethyl 2-(6-(4-chlorophenoxy)hexyl)oxirane-2-carboxylate
Request Quote
| Product | Product Code | Pricing |
|---|
(R)-Ethyl 2-(6-(4-chlorophenoxy)hexyl)oxirane-2-carboxylate
CAS Number:
124083-20-1 | OMXX-278646-01 | Pricing > |
Product Information
| Chemical Formula: | C17H23ClO4 |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 326.82 |
|---|
| Synonyms: | S-(+)-Etomoxir;(S)-2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]Oxiranecarboxylic Acid, Ethyl Ester;R-(+)-Etomoxir;(R)-2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]Oxiranecarboxylic Acid, Ethyl Ester;2-Oxiranecarboxylic Acid, 2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]-, Ethyl Ester, (2R)-(R)-(+)-Etomoxir;(R)-2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]Oxirane-2-Carboxylic Acid Ethyl Ester;2-Oxiranecarboxylic Acid, 2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]-, Ethyl Ester, (2R)-;(2S)-2-[6-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Hexyl]Oxirane-2-Carboxylic Acid Ethyl Ester |
|---|
| MDL No.: | MFCD11227266 |
|---|
| EINECS / EC No.: | N/A |
|---|
| Pubchem CID: | 9840324 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name: | ethyl (2R)-2-[6-(4-chlorophenoxy)hexyl]oxirane-2-carboxylate |
|---|
| Standard InchI: | InChI=1S/C17H23ClO4/c1-2-20-16(19)17(13-22-17)11-5-3-4-6-12-21-15-9-7-14(18)8-10-15/h7-10H,2-6,11-13H2,1H3/t17-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InchI Key: | DZLOHEOHWICNIL-QGZVFWFLSA-N |
|---|
| SMILES: | CCOC(=O)C1(CO1)CCCCCCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl |
|---|
| Appearance: | - |
|---|
| Melting Point: | 32-34 °C |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | 405.029 °C at 760 mmHg |
|---|
| Density (Theoretical): | 1.163 |
|---|
| Refractive Index: | 1.52 |
|---|
Safety Information
| Signal Word: | Warning |
|---|
| Hazard Statements: | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
|---|
| Precautionary Statements: | P261-P305+P351+P338 |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 142.6 °C |
|---|
| Transportation Information: | N/A |
|---|
| GHS Pictograms: |  |
|---|
��
See more Carbon products. Carbon (atomic symbol: C, atomic number: 6) is a Block P, Group 14, Period 2 element. 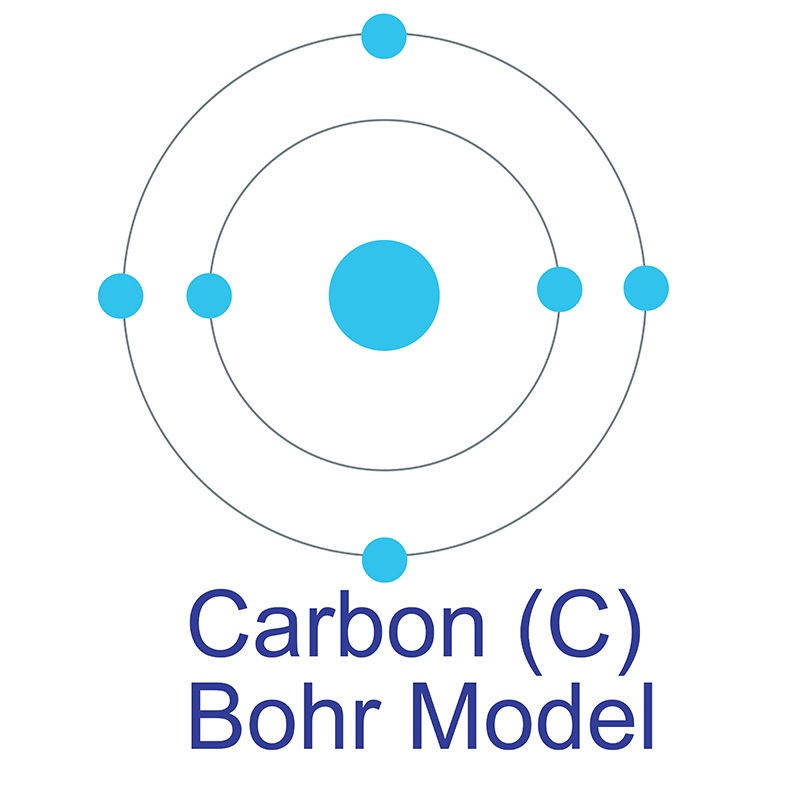 The number of electrons in each of Carbon's shells is 2, 4 and its electron configuration is [He] 2s2 2p2. In its elemental form, carbon's CAS number is 7440-44-0. Carbon is at the same time one of the softest (graphite) and hardest (diamond) materials found in nature. It is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element (by mass) in the universe after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon was discovered by the Egyptians and Sumerians circa 3750 BC. It was first recognized as an element by Antoine Lavoisierby in 1789.
The number of electrons in each of Carbon's shells is 2, 4 and its electron configuration is [He] 2s2 2p2. In its elemental form, carbon's CAS number is 7440-44-0. Carbon is at the same time one of the softest (graphite) and hardest (diamond) materials found in nature. It is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element (by mass) in the universe after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon was discovered by the Egyptians and Sumerians circa 3750 BC. It was first recognized as an element by Antoine Lavoisierby in 1789.
 The number of electrons in each of Carbon's shells is 2, 4 and its electron configuration is [He] 2s2 2p2. In its elemental form, carbon's CAS number is 7440-44-0. Carbon is at the same time one of the softest (graphite) and hardest (diamond) materials found in nature. It is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element (by mass) in the universe after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon was discovered by the Egyptians and Sumerians circa 3750 BC. It was first recognized as an element by Antoine Lavoisierby in 1789.
The number of electrons in each of Carbon's shells is 2, 4 and its electron configuration is [He] 2s2 2p2. In its elemental form, carbon's CAS number is 7440-44-0. Carbon is at the same time one of the softest (graphite) and hardest (diamond) materials found in nature. It is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element (by mass) in the universe after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon was discovered by the Egyptians and Sumerians circa 3750 BC. It was first recognized as an element by Antoine Lavoisierby in 1789.