About Manganese
Manganese is a hard and brittle paramagnetic metal that oxidizes easily, and is found most commonly as manganese dioxide, a black mineral that historically was known as magnes, magnesia, or magnesia negra, all names derived from the origin of the minerals in the Magnesia region of the area known in modern times as Greece.
The dark color of manganese dioxide lent it to use in pigments, an application with a history dating back to stone age cave paintings. Manganese compounds were also used by glassmakers in ancient Egypt and Rome to tint or decolorize glass, a practice that continued into modern times. Use in glassmaking made manganese dioxide easy to obtain for alchemists and early chemists who used it to produce chlorine-containing bleaching agents and other useful lab reagents. Some of these chemists recognized that the compound contained a new element, but the first to actually isolate manganese metal was Johan Gottlieb Gahn, who accomplished the task in 1774. Spartan steel weapons had an unusually high level of manganese, and though it is debated whether its introduction was purposeful or an accident of working with manganese-rich ores, it is known that this was responsible for the notable hardness of Spartan steel. In the early 19th century, this effect was rediscovered and manganese use in steelmaking became commonplace.
Manganese remains very important in the production of alloys. Manganese can be used in corrosion resistant formulations such as stainless steel, and is also added in order to improve workability and tensile strength. In aluminum alloys, manganese is added primarily to prevent corrosion. Manganese may also be used as a finishing coating on objects made of ferrous metals, deposited through a process called phosphating. Manganese salts are dissolved in a solution of phosphoric acid, and the object to be coated is submerged in the liquid. Magnesium is then deposited in a thin layer on the surface. The coating is useful for providing corrosion resistance, though in modern uses it usually does so in combination with further coating or painting of the surface.
After use in metalworking, the largest use of manganese is in batteries. Manganese dioxide was first used in the Leclanche cell battery design in 1866; versions of this battery powered early telegraphy and signaling devices. The same compound is still used in modern zinc-carbon and alkaline batteries.
Additional uses of manganese rely on some of its other notable properties. Due to the wide range of possible oxidation states for the element, manganese compounds exhibit a variety of colors. Many of these have historically found use as pigments. Additionally, any manganese compounds are strong oxidizing agents, and have historically been used in organic synthesis and industrial applications. Manganese oxide has been used in glassmaking to oxidize iron contaminants that otherwise lend a green tinge to the final product. Potassium permanganate is used similarly in water treatment to react with and remove iron and hydrogen sulfide contamination, and can also be used as an antiseptic. Methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl is an organometallic compound used to increase the octane rating of gasoline and reduce engine knocking.
Manganese is a key component of several materials with rare electromagnetic properties that are potentially useful for new technologies. Manganese-based perovskite oxides exhibit colossal magnetoresistance (CMR)--a change in electrical resistance of the material by orders of magnitude when the material is introduced into a magnetic field. Magnetoresistance is currently exploited in technology such as computer hard drives, but current materials show a much smaller change in resistance than is seen with CMR. Ongoing research into CMR hopes to eventually use it to improve upon current technologies. Manganese can also be a component of magnetic semiconducting materials such as gallium manganese arsenide, that have applications in fields such as spintronics.
Manganese is an essential trace nutrient for all known forms of life because it serves as a cofactor for many essential metabolic enzymes. However, an excess of manganese, particularly in certain forms such as inhaled dusts and fumes, can be toxic.
The primary ore of manganese is pyrolusite, the mineral name of manganese dioxide. This and other manganese ores are leached with sulfuric acid to extract manganese in solution, followed by use of an electrowinning process to produce pure manganese. Alternatively, manganese ores can be mixed with other ores and carbon in a blast furnace to produce ferromanganese or silicomanganese.
Products
Manganese is a key metal alloy component, particularly in stainless steels. It is used to both colorize and decolorize glass.  Potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidizing
Potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidizing  agent that is used in medicine and manganese oxide is used in dry cell batteries. Manganese is also added as a nutritional supplement for both human and animal consumption. Manganese is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Manganese nanoparticles and nanopowders are also available. Manganese oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Manganese fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Manganese is also available in soluble forms including manganese chloride, manganese nitrate, and manganese acetate. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
agent that is used in medicine and manganese oxide is used in dry cell batteries. Manganese is also added as a nutritional supplement for both human and animal consumption. Manganese is available as metal and compounds with purities from 99% to 99.999% (ACS grade to ultra-high purity). Elemental or metallic forms include pellets, rod, wire and granules for evaporation source material purposes. Manganese nanoparticles and nanopowders are also available. Manganese oxides are available in powder and dense pellet form for such uses as optical coating and thin film applications. Oxides tend to be insoluble. Manganese fluorides are another insoluble form for uses in which oxygen is undesirable such as metallurgy, chemical and physical vapor deposition and in some optical coatings. Manganese is also available in soluble forms including manganese chloride, manganese nitrate, and manganese acetate. These compounds can be manufactured as solutions at specified stoichiometries.
Manganese Properties
 Manganese is a Block D, Group 7, Period 4 element.
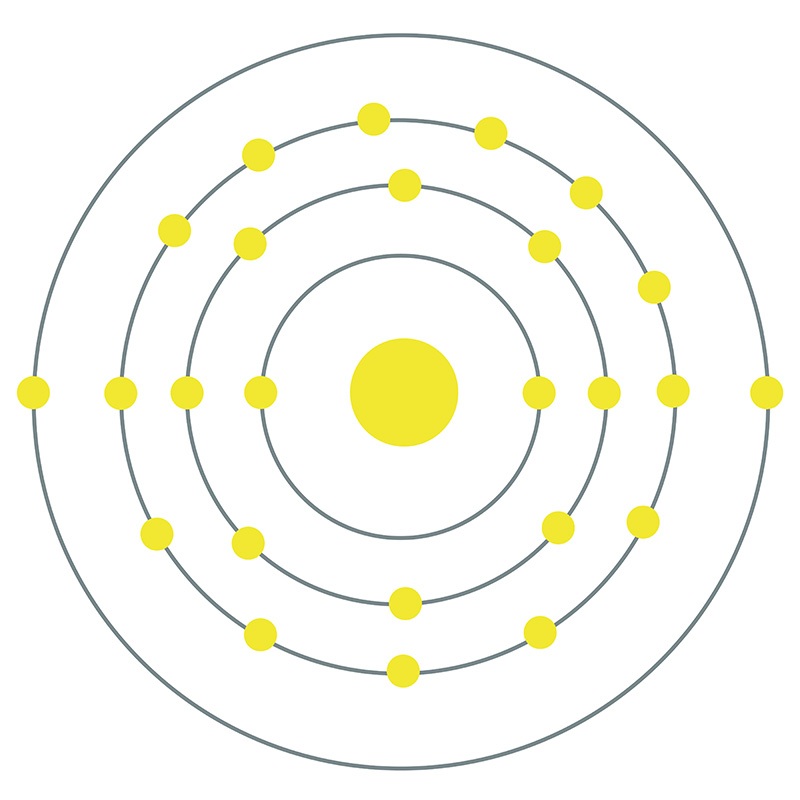
Manganese is a Block D, Group 7, Period 4 element. 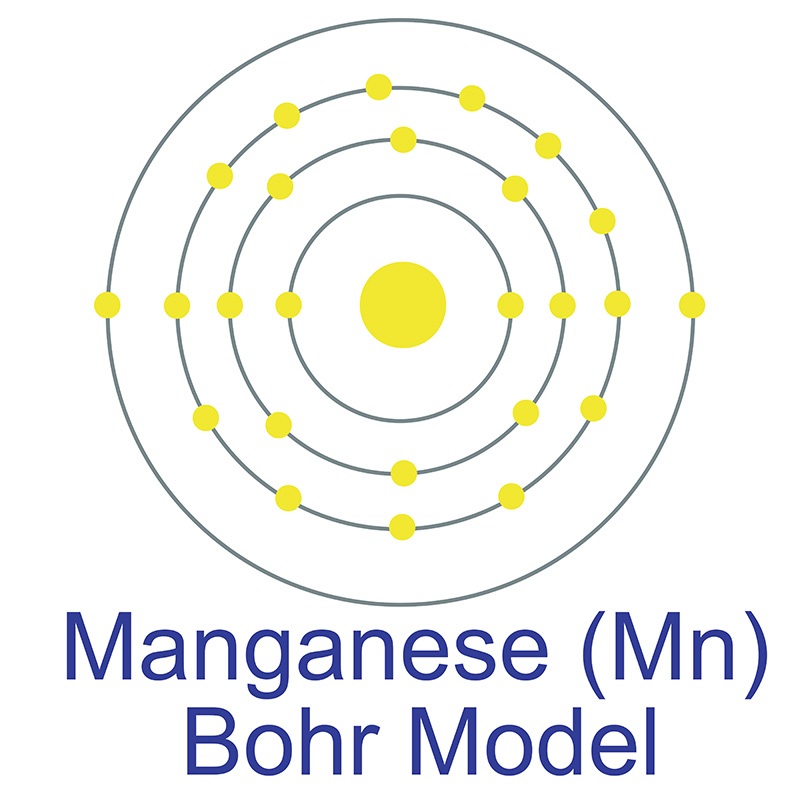 The number of electrons in each of Manganese's shells is 2, 8, 13, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d5 4s2. The manganese atom has a radius of 136.7.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 200.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7439-96-5, manganese has a silvery metallic appearance.
The number of electrons in each of Manganese's shells is 2, 8, 13, 2 and its electron configuration is [Ar] 3d5 4s2. The manganese atom has a radius of 136.7.pm and its Van der Waals radius is 200.pm. In its elemental form, CAS 7439-96-5, manganese has a silvery metallic appearance.  Manganese is found as a free element in nature and also in the minerals pyrolusite MnO2, braunite (Mn2+Mn3+6)(SiO12), psilomelane (Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10 and rhodochrosite MnCO3. Manganese was first discovered by Torbern Olof Bergman in 1770 and first isolated by Johann Gottlieb Gahn in 1774. The name Manganese originates from the Latin word mangnes meaning magnet.
Manganese is found as a free element in nature and also in the minerals pyrolusite MnO2, braunite (Mn2+Mn3+6)(SiO12), psilomelane (Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10 and rhodochrosite MnCO3. Manganese was first discovered by Torbern Olof Bergman in 1770 and first isolated by Johann Gottlieb Gahn in 1774. The name Manganese originates from the Latin word mangnes meaning magnet.
Health, Safety & Transportation Information for Manganese
Manganese in excess is toxic, particularly the inhalation of manganese in powder or dust form. Safety data for Manganese and its compounds can vary widely depending on the form. For potential hazard information, toxicity, and road, sea and air transportation limitations, such as DOT Hazard Class, DOT Number, EU Number, NFPA Health rating and RTECS Class, please see the specific material or compound referenced in the Products tab. The below information applies to elemental (metallic) Manganese.
| Safety Data | |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H260 |
| Hazard Codes | F |
| Risk Codes | 11-15 |
| Safety Precautions | 43 |
| RTECS Number | OO9275000 |
| Transport Information | UN 3208 4.3/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | nwg |
| Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling (GHS) |
|
Manganese Isotopes
Naturally occurring Manganese has 1 stable isotope: 55Mn.
| Nuclide | Isotopic Mass | Half-Life | Mode of Decay | Nuclear Spin | Magnetic Moment | Binding Energy (MeV) | Natural Abundance (% by atom) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44Mn | 44.00687(54)# | <105 ns | p to 43Cr | (2-)# | N/A | 321.82 | - |
| 45Mn | 44.99451(32)# | <70 ns | p to 44Cr | (7/2-)# | N/A | 341.08 | - |
| 46Mn | 45.98672(12)# | 37(3) ms | ß+ to 46Cr; ß+ + p to 45V; ß+ + a to 42Ti; ß+ + 2p to 44Ti | (4+) | N/A | 356.61 | - |
| 47Mn | 46.97610(17)# | 100(50) ms | ß+ to 47Cr; ß+ + p to 46V | 5/2-# | N/A | 374.01 | - |
| 48Mn | 47.96852(12) | 158.1(22) ms | ß+ to 48Cr; ß+ + p to 47V; ß+ + a to 44Ti | 4+ | N/A | 389.54 | - |
| 49Mn | 48.959618(26) | 382(7) ms | p to 49Cr | 5/2- | N/A | 406 | - |
| 50Mn | 49.9542382(11) | 283.29(8) ms | p to 50Cr | 0+ | N/A | 418.74 | - |
| 51Mn | 50.9482108(11) | 46.2(1) min | EC to 51Cr | 5/2- | N/A | 432.41 | - |
| 52Mn | 51.9455655(21) | 5.591(3) d | EC to 52Cr | 6+ | 3.063 | 443.28 | - |
| 53Mn | 52.9412901(9) | 3.74(4)E+6 y | EC to 53Cr | 7/2- | 5.024 | 455.09 | - |
| 54Mn | 53.9403589(14) | 312.03(3) d | EC to 54Cr; ß- to 54Fe | 3+ | 3.282 | 464.1 | - |
| 55Mn | 54.9380451(7) | STABLE | - | 5/2- | 3.4532 | 474.04 | 100 |
| 56Mn | 55.9389049(7) | 2.5789(1) h | ß- to 56Fe | 3+ | 3.2266 | 482.12 | - |
| 57Mn | 56.9382854(20) | 85.4(18) s | ß- to 57Fe | 5/2- | N/A | 490.2 | - |
| 58Mn | 57.93998(3) | 3.0(1) s | ß- to 58Fe | 1+ | N/A | 497.34 | - |
| 59Mn | 58.94044(3) | 4.59(5) s | ß- to 59Fe | (5/2)- | N/A | 504.49 | - |
| 60Mn | 59.94291(9) | 51(6) s | ß- to 60Fe | 0+ | N/A | 510.71 | - |
| 61Mn | 60.94465(24) | 0.67(4) s | ß- to 61Fe | (5/2)- | N/A | 516.92 | - |
| 62Mn | 61.94843(24) | 671(5) ms | ß- to 62Fe; ß- + n to 61Fe | (3+) | N/A | 521.27 | - |
| 63Mn | 62.95024(28) | 275(4) ms | ß- to 63Fe | 5/2-# | N/A | 527.49 | - |
| 64Mn | 63.95425(29) | 88.8(25) ms | ß- to 64Fe; ß- + n to 63Fe | (1+) | N/A | 531.84 | - |
| 65Mn | 64.95634(58) | 92(1) ms | ß- to 65Fe; ß- + n to 64Fe | 5/2-# | N/A | 538.06 | - |
| 66Mn | 65.96108(43)# | 64.4(18) ms | ß- to 66Fe; ß- + n to 65Fe | N/A | N/A | 541.48 | - |
| 67Mn | 66.96414(54)# | 45(3) ms | ß- to 67Fe | 5/2-# | N/A | 546.76 | - |
| 68Mn | 67.96930(64)# | 28(4) ms | Unknown | N/A | N/A | 550.18 | - |
| 69Mn | 68.97284(86)# | 14(4) ms | Unknown | 5/2-# | N/A | 555.46 | - |